
Olympus Plan Achromatic Objectives are designed for clinical laboratory or examination applications. When using brightfield observation in a transmitted illumination system, Olympus Plan Achromatic Objectives provide excellent field flatness of up to F.N.22.
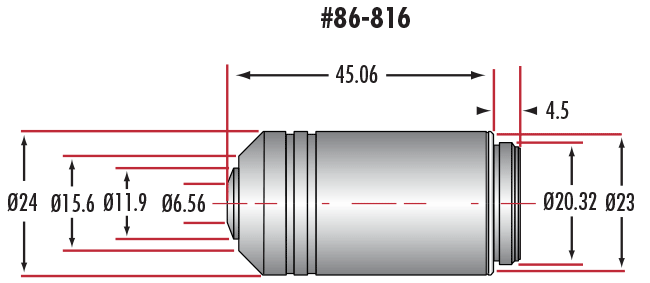
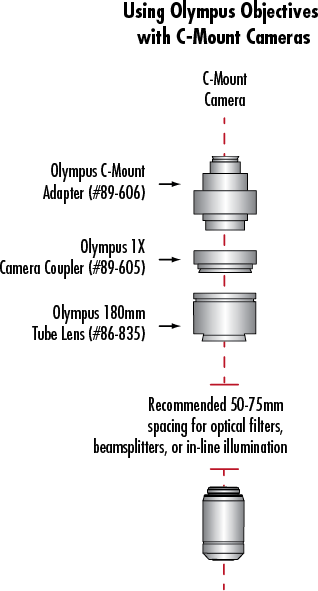
| Title | Compare | Stock Number | Price | Buy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olympus Single Port Tube Lens, 180mm Focal Length | #86-835 | £607.75 Request Quote |
|
||
| Olympus Wide Field Tube Lens, 180mm Focal Length | #36-401 | £450.50 Request Quote |
|
||
| Olympus Wide Field Tube Lens to T-Mount Holder | #11-149 | £130.90 Request Quote |
|
||
| Olympus Low Auto Fluorescence Immersion Oil | #86-834 | £63.75 Request Quote |
|
||
| Olympus 1X Camera Coupler | #89-605 | £97.75 Request Quote |
|
||
| Olympus C-Mount Adapter | #89-606 | £199.75 Request Quote |
|
||
| Filter Cube for Olympus BX2/IX2 Microscopes | #86-832 | £522.75 Request Quote |
|
||
| Filter Cube for Olympus BX3/IX3 Microscopes | #86-833 | £522.75 Request Quote |
|
1-800-363-1992
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2025 | Edmund Optics, Ltd Unit 1, Opus Avenue, Nether Poppleton, York, YO26 6BL, UK
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act